Is Dermarolling Safe for Photodamage Skin? Doctors Point of View
Why Photodamage skin is the usual complaint in the Clinics?
Is dermarolling or microneedling therapy effective in treating photodamage skin?
What is the Role of Microneedling in Treating Photodamaged Skin?
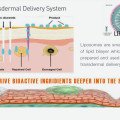
One of the uses of microneedling is the efficient absorption of topical medicines. This is the principle used behind in treating photodamaged skin. Clinicians were able to prove that topical applications of serum can be best applied through the help of skin needling. The main goal of topical medication is to improve the penetration of substances that is important for optimization and development of cosmetic medicine.
There are three possible routes for skin penetration, these are follicular, intercellular and transcellular. The skin functions as an important barrier to the penetration of foreign or exogenous substances into the body.
It is also a potential route for the transport of functional and active principles into the hair and skin. Before it was assumed that the intercellular route was the only possible penetration pathway for substances applied topically. The transfollicular path was largely ignored because the hair follicles comprise only of 0.1% of the total skin.
Recent studies have shown that follicular penetration stressed that hair follicles is an efficient penetration and highly relevant pathway. It also serves as reservoir for substances that are applied topically. Thus, hair follicles are an interesting target area for topical applications.
More so, it is closely surrounded by antigen-presenting cells and capillaries that are associated with host stem cells and sebaceous glands in the bulge regioon.
Melanin is a natural pigment of the skin. It gives the hair and skin their color. Laser hair removal for instance, relies on selective photothermolysis using melanin as the chroomophore. Loading melanin in the hair follicles can improve the effectiveness of laser in subjects with white, gray and blonde hairs.
However, the effective penetration of melanin through the hair and skin is hindered due to its hydrophilic nature and high molecular weight. Thus, encapsulation of melanin in liposomes may improve its penetration on the inside structure of the hair.
Recently, microneedling has been described as a novel technique used to increase transdermal absorption of topical drugs. A study used microneedling device to apply melanin liposomes into human hair skin to improve transfollicular absorption.
Skin needling has been found useful to enhance the penetration of ALA or amino levulinic acid or MAL or methyl amino levulinate for photodynamic therapy (PDT). In a study, 21 patients with photoaging was treated using photodynamic therapy using broadband-pulsed light and 630 nm light after1 hour ALA incubation period and multiple passes of manual roller.
The pretreatment prior to the application of ALA appears to be well tolerated. It also allows even absorption or deeper penetration of ALA following the mentioned incubation period.
Another study uses microneedling-assisted photodynamic therapy to enhance the penetration of MAL into the epidermis for patients having solar keratosis. The improvement was more pronounced on the skin needling assistive site.
Therefore, researchers concluded that microneedling treatment can produce cosmetic results that are superior to those of conventional MAL-PDT for improving the appearance of photodamaged skin. The results were also similar for the reduction of actinic keratosis.
What are the effective topical serums for photodamage skin?
There is existing controversy whether topical antioxidants are effective in protecting against and reversing photodamage skin. Topical vitamins such as C, and E, and topical selenium are known for its protective effect against suntan, sun burn, and skin cancer. It can also reverse the appearance of wrinkles caused by photo aging and mottled pigmentation.
However, there are certain forms of these antioxidants that are considered active and stable after percutaneous absorption. For better and effective topical application, Vitamin C should be non-esterefied, optimally at 20% concentration, and must be acidic. Vitamin E should also be non-esterified isomer d-alpha- tocopherol at 2% to 5% concentration.
Selenium is percutaneously absorbed and become active when applied topically as I-selenomethionine. The key note here is that the antioxidants should be applied only to the skin when it is on its active formulation.
First, your skin attains higher levels of each antioxidant that can be achieved if these vitamins are taken orally. The vitamin C level is attained in the skin through topical application is 20 to 40 times than that achievable with an oral Vitamin C. The same thing goes with topical application of Vitamin E in the skin; it increases the absorption by a factor of 10.6 and selenium by 1.7.
More so, topical applications in the arms with a reservoir of antioxidants cannot easily be rubbed off or washed out. This is a kind of protection that stays in the skin for several days even after application.
This is the reason why Microneedling therapy is an effective treatment for photodamage skin because it helps in faster absorption of topical agents and serum. Using it together with topical agents and serum will further enhance its effectiveness in improving the appearance of photodamage skin.






Please add your thoughts
Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!