How Calcium Combined with Ascorbic Acid and Microneedling Can Treat Stretch Marks?
Some individuals suffer negative psychological impact because of stretch marks. There are several methods available used to treat stretch marks but there is lacking of high quality evidence supporting its use. In here, you will learn the combined therapy of calcium, ascorbic acid and microneedling in managing stretch marks. Injections of diluted calcium hydroxylapatite filler combined with topical ascorbic acid and microneedling are used to treat white and red striae.
Why stretch marks develop? Can they still be removed?
Stretch marks are called in medical term as striae distensae which are permanent type of dermal scarring. It has an unattractive appearance that may cause significant psychological and negative impact on some individuals. The exact cause of stretch marks is unknown.
The incidence of stretch marks is associated with abrupt changes in weight, use of corticosteroids and rapid growth. More so, it occurs primarily among pregnant women, obese individuals and adolescents. Approximately, 90 percent of pregnant women develop stretch marks by third trimester. It is commonly seen on their breast or abdomen.
The striae generally follow cleavage lines that transverse to the direction with the greatest tension. It appears where the tissue is weakest and on areas that are least able to withstand mechanical stress. Initially, it appears as red or striae rubrae and later becoming more atrophic and white or striae albae.
If you view it in the microscope, you will observe inflammatory changes that are initially evident with perivascular lymphocytic cuffing and dermal edema. It is then followed with loss of rete ridges and epidermal atrophy. Stretch marks can be distinguished from normal skin by dense packed areas of horizontally arranges and thin bundles of collagen lying parallel to skin surface.
As compared with normal skin, the numbers of vertical fibrillin fibers that are adjacent to elastin fibers in the papillary dermis and in dermal epidermal junction are significantly reduced in areas with stretch marks. There are a number of methods used to treat stretch marks including creams and lotions containing various vitamins, plant extracts, and proteins.
Other treatment includes topical ascorbic acid, glycolic acid peels, microneedling, microdermabrasions, lasers, intensed pulse light, tretinoin 0.1 cream and injections of autologous pluripotent cells. However there is lacking or limited high quality evidence for long-lasting and effective therapies. There are no consensus guidelines in treating striae.
The lack of permanent and effective treatment results can be due to poor improvement of skin color or permanence of skin atrophy.
How a combination therapy of microneedling, ascorbic acid and calcium reduces stretch marks?
Microneedling or also known as dermarolling therapy is a method used to treat stretch marks. It works by stimulating the intradermal collagen production. It is also a means of achieving trans-epidermal drug delivery.
Ascorbic acid on the other hand, also enhances or stimulates the production of normal collagen. It can be delivered thru transdermal drug delivery via skin needling. In recent years, poly L-lactic acid fillers and hyaluronic acid fillers are used to improve the skin depression associated with atrophic acne scars. It is also used to improve appearance of atrophic stretch marks.
Another type of dermal filler is calcium hydroxylapatite (caHA) composed of white 25–45 µM microspheres of caHA suspended in gel carrier. Calcium hydroxylapatite is considered as a biostimulator because of its ability to induce neoelastogenesis, angiogenesis or formation of new blood vessels and neocollagenesis and dermal filler. Presently, there are no reports regarding the use of CaHA filler in treating atrophic striae.
To address this concern, a study of Casabona and Marchese (2017) was made to treat dyspigmentation and skin atrophy associated with stretch marks. Participants who came into the clinic with striae were treated with a combination of 1:1 intradermal and subdermal injections of diluted calcium hydroxylapatite, topical ascorbic acid and microneedling. The main objective of the study is to evaluate the effectiveness of combined therapy for improving the appearance of white and red stretch marks.
Is microneedling combined with ascorbic acid and calcium effective in treating stretch marks?
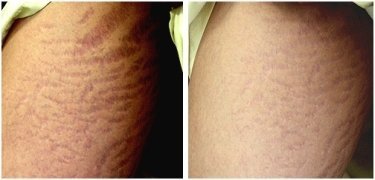
After months of treatment and using the Manchester Scar Scale Scores, the results showed significant aesthetic improvement in striae appearance. Suprisingly, the clinical improvements were correlated with patient’s satisfaction.
Skin biopsies were done and revealed an increase quality and quantity of elastin fibers and dermal collagen in areas treated with the combination therapy of microneedling, ascorbic acid and calcium, as compared with the untreated skin. The combined treatments are also well tolerated. The reported adverse effects from the combined treatments reflect individual treatment.
Whatever the type of treatment used, the goal for managing atrophic appearance of stretch marks is to induce collagen production. Dermal filler injections and microneedling stimulates production of collagen thru signal transduction cascade that follows after skin trauma. The wound healing process occurs in a predictable phases.
How dermarolling or microneedling stimulates collagen and elastin production?
The initial injury caused by skin needling distrupts the vascular endothelium resulting in the activation of platelet. It is then followed by the release of growth factors. Subsequently, an influx of inflammatory polymorphonuclear leukocytes followed. Together with the endothelial cells and fibroblasts, an aggregate of fibrin framework is formed thru platelet activation.
The secretion of additional growth factors and cytokines promote fibroblast proliferation, formation of new blood vessels or angiogenesis and migration of keratinocytes. In the proliferation stage, fibroblast is the one responsible for the organization of extracellular matrix and production of elastin. Fibroblast multiplies increasing the production of collagen type III which is then converted to collagen type I that lead to tightening of the skin.
Microneedling treatment promotes the removal of damaged and old collagen and increases the synthesis or formation of new collagen beneath the epidermis. The tightening of the skin will lead to better appearance of stretch marks and improve atrophy.
Skin needling also enhances the delivery of medications like ascorbic acid into the skin. Vitamin C or ascorbic acid is essential in producing normal collagen. It is an essential cofactor for the enzymes which are required for processing collagen type I and III. Vitamin C stimulates collagen production in the dermis by increasing the proliferation of fibroblast. Therefore, it seems likely that vitamin C can improve the appearance of stretch marks.
For over a decade, CaHA is used for facial rejuvenation to correct moderate to severe wrinkles and soft tissue volume loss. When injected superficially in diluted form, it demonstrates effectiveness in treating skin laxity and volume loss.
In conclusion
Microneedling, topical Vitamin C, and diluted calcium hydroxylapatite can increase the production of collagen in the skin. Combining these procedures presents an effective and safe treatment for white and red stretch marks.
Bibliography
Gabriela Casabona, MDcorresponding author and Paula Marchese, MD. (2017).
Calcium Hydroxylapatite Combined with Microneedling and Ascorbic Acid is Effective for Treating Stretch Marks. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. , 1474.




Please add your thoughts
Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!